Nvidia GPU¶
GPGPU: General-purpose computing on graphics processing units Nvidia: Company that design graphics processing units (GPUs) for the gaming and professional markets. Nvidia GPU have better ecosystem for Machine Learning.
Common commands¶
Monitor GPU¶
nvidia-smiwatch -n 1 nvidia-sminvcc --version # check CUDA version with nvcc
Path¶
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/cuda/bin/:/usr/local/cuda/extras/CUPTI/lib64/
boost GPU¶
nvidia-smi -q -d CLOCK # check clock speed
nvidia-smi -pm 1 # persistence mode
nvidia-smi -q -d SUPPORTED_CLOCKS # supported clock rate
sudo nvidia-smi -ac 5001,1590 # Specifies <memory,graphics> application clocks, 5001, 1590 for Tesla T4
profile GPU usage¶
nsys profile [application] [application arg] # Nsight system, (a client with GUI required)
nv-nsight-cu-cli --metrics xxx [application] [application arg] # Nsight Compute, for kernel
nsys profile
# if pyTorch missing so, add LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/lib64/python3.6/site-packages/torch/lib in front of nv-nsight-cu-cli
# Legacy
nvprof -m tensor_precision_fu_utilization [application] [application arg]
Common setting for set up GPU instance on cloud¶
Since ISA limit the permission, need to ask ISA to setup VM. Below is some general requirements that I usually need to pre-install.
- instance type (For AWS, g4 for T4, p3 for V100, p3 not available in HK)
- OS: Ubuntu / Centos
- mount SSD/ harddisk
- network: better connect to local machine for transfering files
- python3
- Nvidia driver which allow user to profile GPU performance counter
modprobe nvidia NVreg_RestrictProfilingToAdminUsers=0- grant permission to access NVIDIA GPU Performance Counters
- CUDA
- cuDNN
- add
/usr/local/cuda/bin/, CUPTI library (/usr/local/<cuda-toolkit>/extras/CUPTI/lib64or/usr/local/<cuda-toolkit>/targets/<arch>/lib) to the path *export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/cuda/bin/:/usr/local/cuda/extras/CUPTI/lib64/ - Optimize clock rate
- pyTorch / tensorflow / the machine learning framework compiled with CUDA
- tmux (for running process in background)
- gcc (if there is any custom layer in network or special software need to be compiled from source, required hours to compile. )
- opencv (for image, could be compiled with CUDA)
- ffmpeg (for video)
GPU Summary Table¶
- Processing Power: GeForce stat from wiki/GeForce_10_series, wiki/GeForce_20_series, Tesla stat from Nvidia
- tensor precision: Tensor Core perform \(D=A \times B + C\), where A, B, C and D are matrices. A and B are half precision 4x4 matrices, whereas D and C can be either half or single precision 4x4 matrices. x8 speed up comparing to FP32 / x4 comparing to FP16. Stat of tensor precision mostly come from Nvidia, such as Turing Whitepaper.
- half precision that slower than single precision consider as not supported.
- Google Cloud Platform(GCP) GPUs Pricing
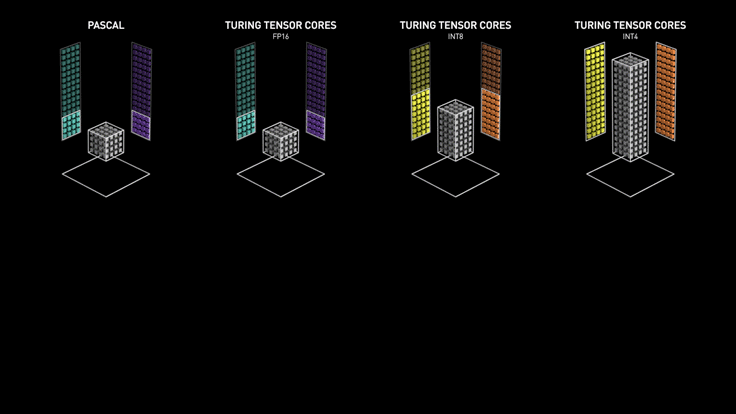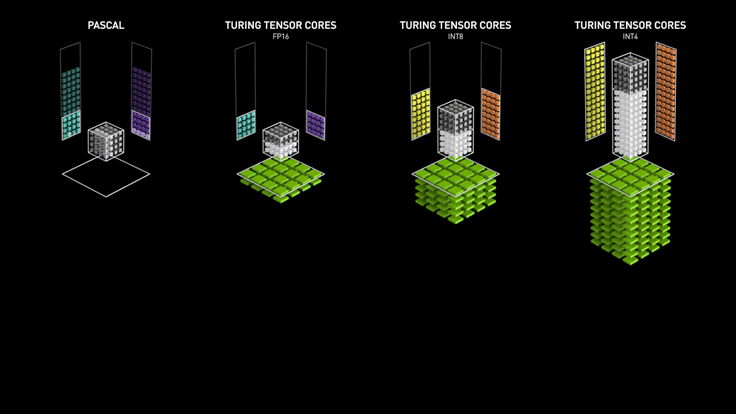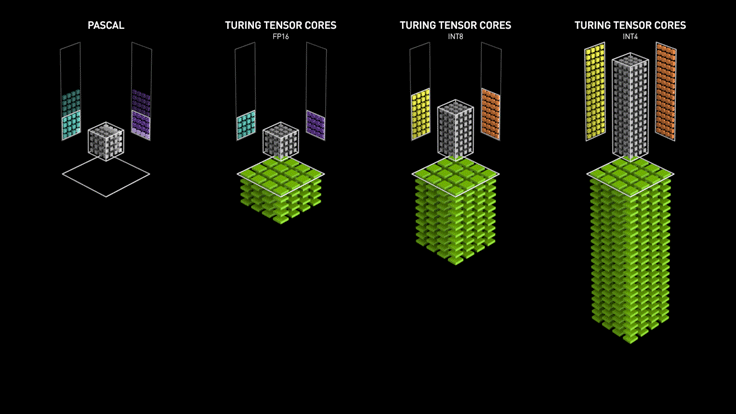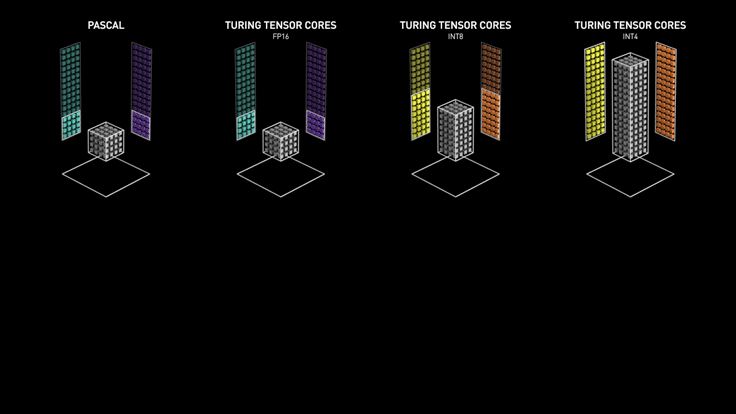
Precision¶
Lower Precision could speed up training and inference time. Precision support matrix
| Ampere | Turing | Volta | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensor Core | FP64, TF32, bfloat16, FP16, INT8, INT4, INT1 | FP16, INT8, INT4, INT1 | FP16 |
| CUDA® Core | FP64, FP32, FP16, bfloat16, INT8 | FP64, FP32, FP16, INT8 | FP64, FP32, FP16, INT8 |
TF datatype preserve bits for exponent (lossing precision):
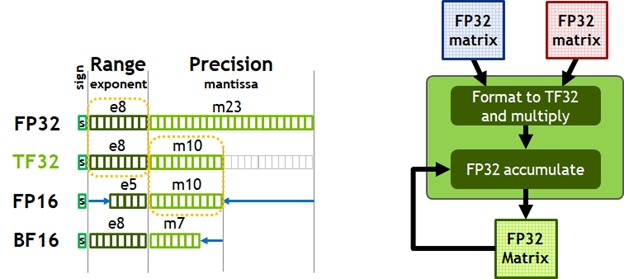 from NVIDIA Ampere Architecture In-Depth
To handle the loss of precision,
from NVIDIA Ampere Architecture In-Depth
To handle the loss of precision,
==Toolkit==¶
CUDA, Compute Unified Device Architecture¶
API for Nvidia’s GPU
Some SOTA papers have its own CUDA code to implement its novel idea, such as deformable convolution in CNN, optical flow wrapper in frame interpolation papers.
nvcc, Nvidia CUDA Compiler¶
CUDA (c++) code compiler, see nvcc C++ Language Support
cuDNN, CUDA Deep Neural Network library¶
GPU-accelerated library for deep neural nets built using CUDA. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. Mainly for neural network framework developer(Caffe, torch etc).torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True which always appear in pyTorch code take advantage of cuDNN to speed up when the model is unchanged.
TensorRT¶
Tensor RunTime
NVIDIA TensorRT™ is an SDK for high-performance deep learning inference. It includes a deep learning inference optimizer and runtime that delivers low latency and high-throughput for deep learning inference applications.
Some training frameworks such as TensorFlow have integrated TensorRT so that it can be used to accelerate inference within the framework. Alternatively, TensorRT can be used as a library within a user application. It includes parsers for importing existing models from Caffe, ONNX, or TensorFlow, and C++ and Python APIs for building models programmatically.
TensorRT Developer Guide
Deploy Model with TensorRT¶
- prepared a pre-trained network with original neural network framework (don’t train on tensorRT)
- Creating a TensorRT network definition from your model
- convert model to TensorRT compatable format (e.g. pyTorch to ONNX, torch2trt)
- define custom layer if TensorRT have not build-in support, e.g. deformable convolution (in cuda)
- Invoking the TensorRT builder to create an optimized runtime engine from the network
- import custom layer
- calibration: for INT8 precision, calibrate via determine the dynamic range of intermediate activations, and hence the appropriate scaling factors for quantization
- Serializing and deserializing the engine so that it can be rapidly recreated at runtime
- Feeding the engine with data to perform inference with TensorRT C++/Python lib
==Others==¶
Mixed Precision training¶
Automatic Mixed Precision, AMP¶
Automatic Mixed Precision for Deep Learning | NVIDIA Developer
For pyTorch, use Apex:
model, optimizer = amp.initialize(model, optimizer, opt_level="O1")
with amp.scale_loss(loss, optimizer) as scaled_loss:
scaled_loss.backward()
if AMP is not available in framework¶
need to find best factor for scaling loss
Optimize model design for Tensor Core¶
- Satisfying Tensor Core Shape Constraints (multiples of 8 for FP16 or 16 for INT8)
- Increasing Arithmetic Intensity, e.g. large channels size (avoid memory bound)
- Decreasing Non-Tensor Core Work
Nvidia Documents¶
CUDA C++ Programing Guide
CUDA C++ Best Practices Guide
CUDA Math API
Mixed Precision Training
An Even Easier Introduction to CUDA¶
- Add Specifier to the code that run on GPU
global: runs on the GPU and can be called from CPU code, kernel
device: runs on the GPU and can be called from GPU code, device code
host: runs on the CPU and can be called from CPU code, host code - Memory Allocation in CUDA
- caller add execution configuration <<<numBlocks, blockSize>>> numBlocks: the number of thread block blockSize: the number of thread in thread block, suggest to be multiple of 32
- in the kernel, assign index for parallel computation
| value | description |
|---|---|
gridDim.x |
the number of blocks in the grid |
blockIdx.x |
the index of the current thread block in the grid |
blockDim.x |
the number of threads in the block |
threadIdx.x |
the index of the current thread within its block |